What is Ultra Processed Food (UPL)?
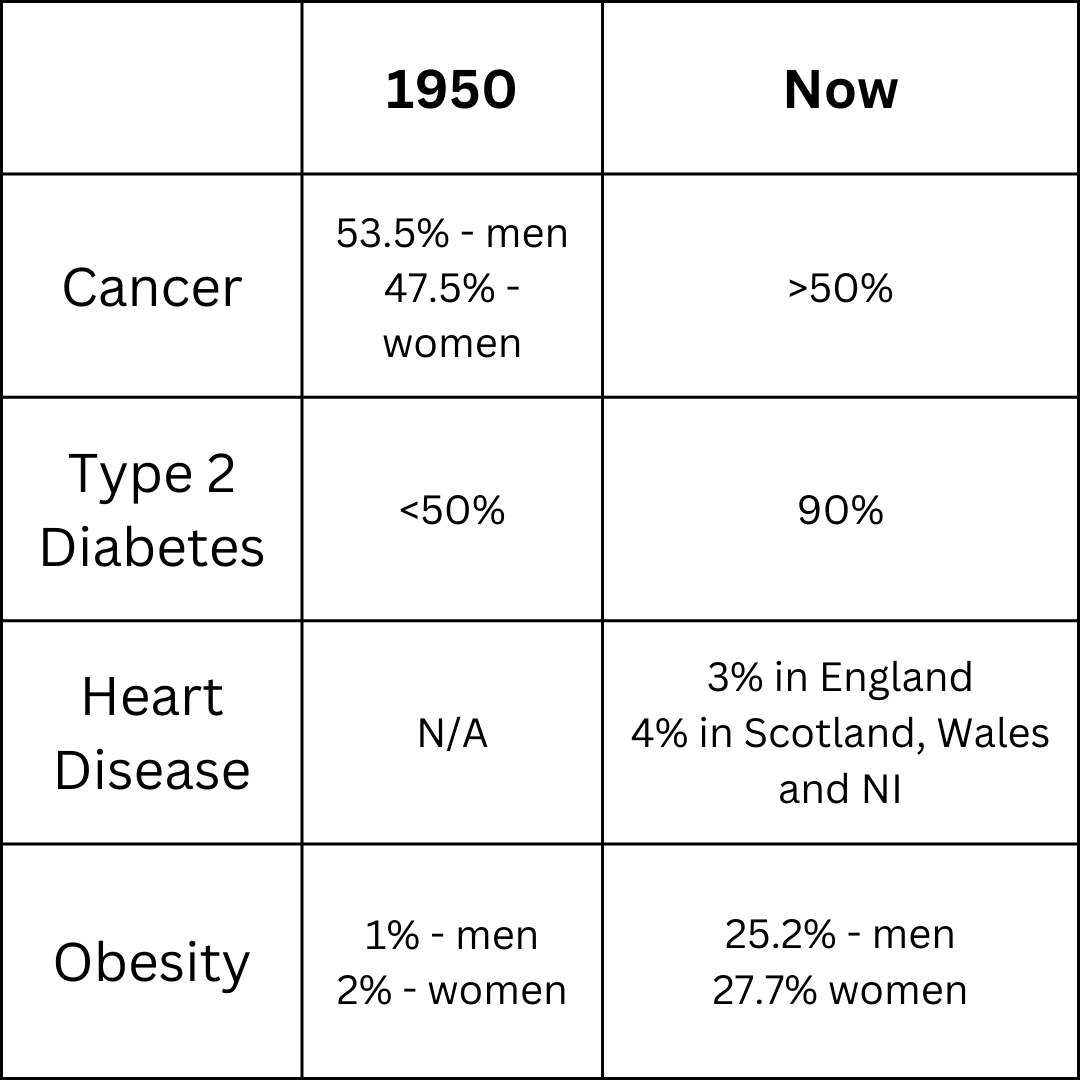
Ultra-processed foods are food products that have undergone extensive processing and often contain a variety of additives, preservatives, and other synthetic ingredients. Ultra-Processed Foods are usually high in sugar, salt, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives, while lacking in essential nutrients, fibre, and vitamins. Examples include sugary snacks, packaged desserts, fast food items, processed meats, instant noodles, and many ready-to-eat meals. Regular consumption of ultra-processed foods has been associated with various health issues, including obesity, heart disease, diabetes, and other chronic conditions.
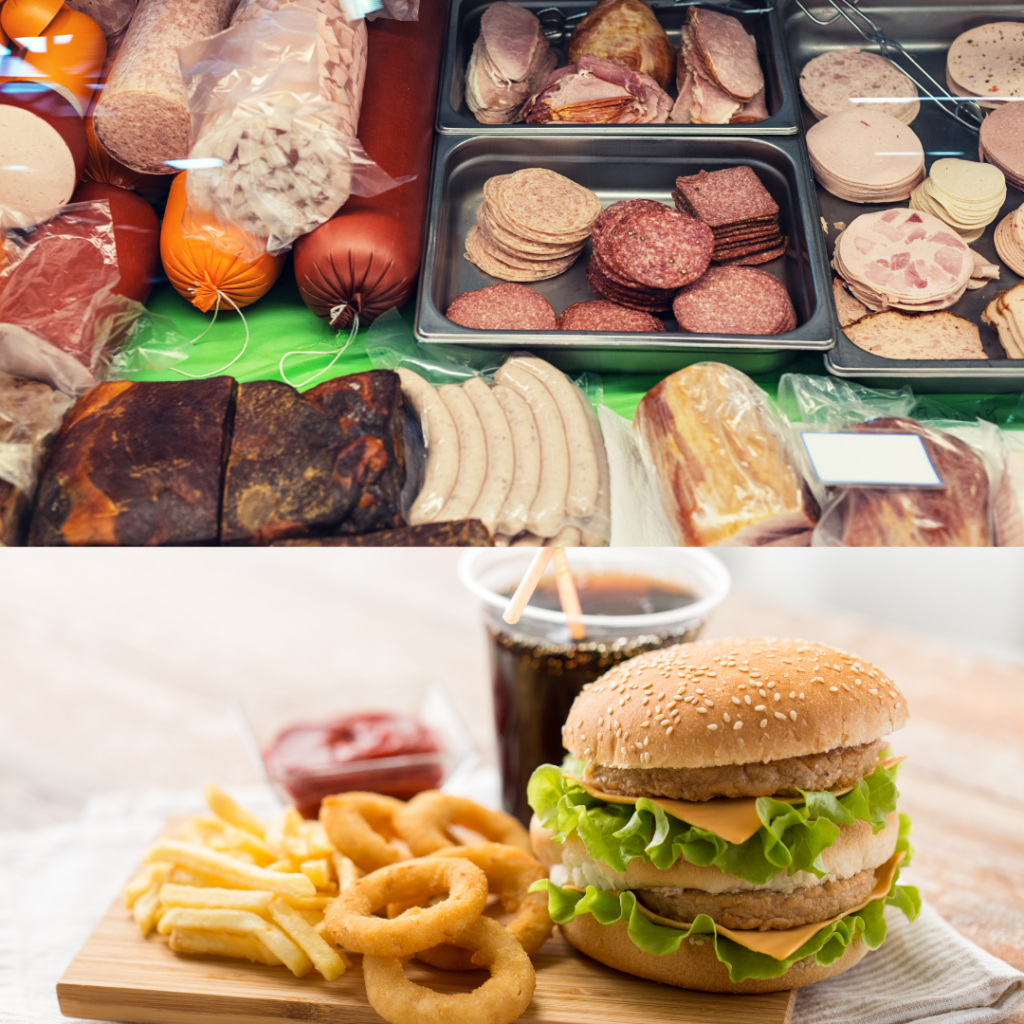

The demand for Ultra Processed Foods
The shift for ultra processed food began in the mid-20th century due to various factors. These include:
Changing Lifestyles: People started turning more to processed foods as a convenient answer as they become busier and had less time for meal preparation.
Marketing and Advertising: Ultra-processed foods were aggressively promoted by the food industry, which emphasised their taste, price, and convenience. Together with vigorous advertising campaigns, this marketing helped these products become widely used.
Economic Factors: When it comes to production and acquisition, ultra-processed meals are frequently less expensive than complete, fresh foods. Thus, consumer preferences for processed foods were influenced by economic factors, particularly for lower-class people.
Technological Advancements: Technological developments in food processing, including canning, refrigeration, and chemical preservatives, have made it possible to produce new food products with better flavour and texture and longer shelf lives. This made it easier to create highly processed foods that were portable, shelf-stable, and easy to eat.
Industrialisation of Food Production: Local, small-scale farming gave way to large-scale, industrialised methods of food production with the arrival of industrialization. Convenience and packaged goods flourished as a result of the ability to produce and distribute food items in large quantities.
Why we need to reduce our dependency on ultra processed foods
Reducing dependency on ultra-processed foods is crucial for several aspects of our health:
Nutritional Concerns: Ultra-processed foods tend to be poor in important nutrients like fibre, vitamins, and minerals and high in unhealthy elements like added sugars, bad fats, sodium, and artificial additives. Overindulgence in certain foods can result in nutritional deficiencies and fuel a host of health issues, such as diabetes, obesity, heart disease, and some types of cancer.
Impact on Health: Regular consumption of ultra-processed foods has been associated with a higher risk of obesity and associated metabolic problems. Because these meals are often high in energy but low in nutrients, they can cause overindulgence in calories without providing enough nourishment, which can lead to weight gain and related health problems.
Dietary Imbalances: An excessive dependence on highly processed foods can result in nutritional imbalances since they frequently take the place of more nutrient-dense whole foods including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. A diet deficient in these vital food groups raises the risk of developing chronic illnesses and jeopardises general health and wellbeing.
Gut Health: Ultra-processed foods may be detrimental to gut health because of their high fibre content, high additive content, and preservative content. Digestion, nutritional absorption, immunological response, and general health depend on the gut microbiota being in a balanced and healthy state. Eating a diet high in highly processed foods might upset this equilibrium and aggravate digestive problems.
Obesity Linked to Processed Foods: What to Avoid in Your Diet (healthline.com): Do you know what you are eating?The Rise of New Age Diseases
“New Age Diseases” is a term that is used to describe medical disorders that have increased in frequency or raised serious issues for the public’s health in recent years. These illnesses frequently correspond with changes in demography, environmental factors, and lifestyle.
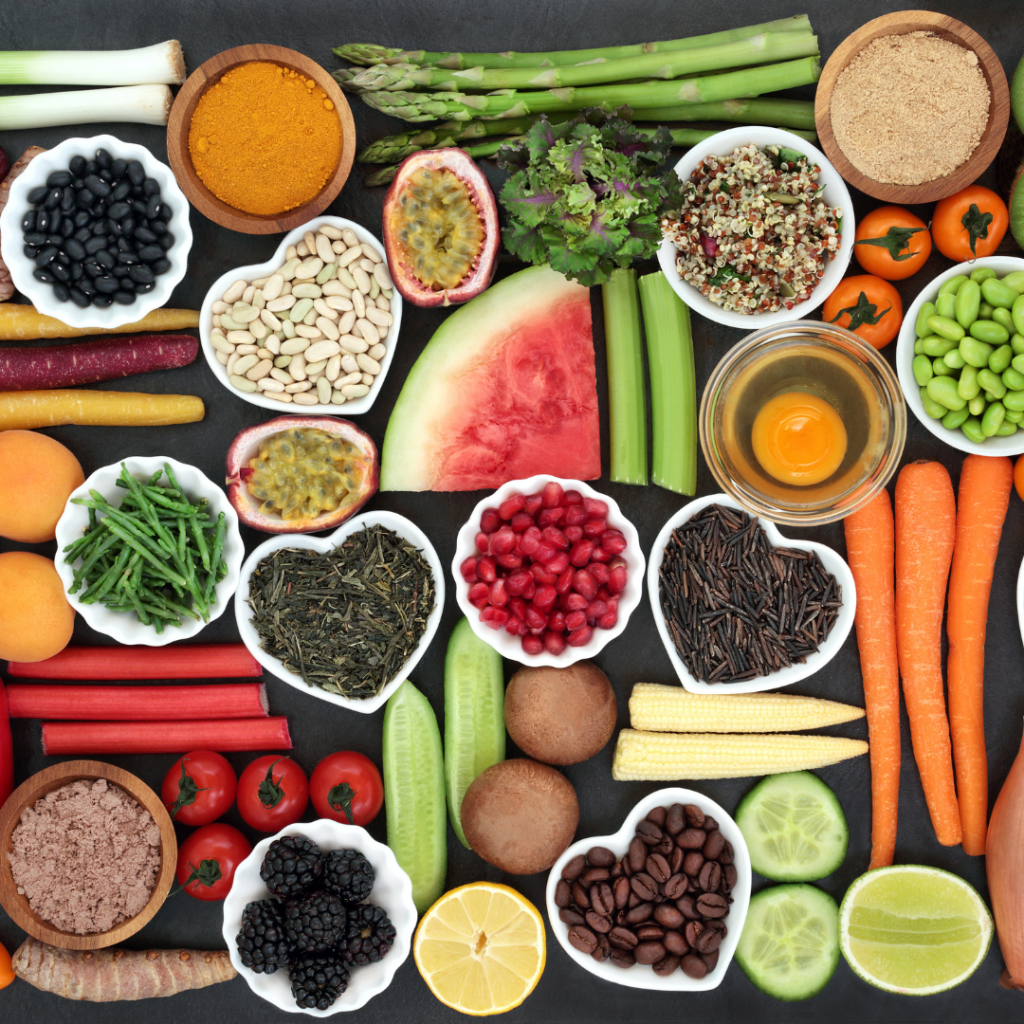
Clean Eating (substitute ultra processed foods)
Clean eating is a dietary approach with a goal to consume whole, minimally processed foods as much as possible. All while avoiding or consuming less highly processed and refined items. Consuming food in its purest form is the main goal, with a concentration on whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Non- Ultra-processed foods list:
- Fruits: Apples, bananas, berries, oranges, kiwi, grapes, mangoes, etc.
- Vegetables: Spinach, kale, broccoli, cauliflower, carrots, bell peppers, tomatoes, cucumbers, etc.
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, oats, barley, bulgur, whole wheat pasta, whole grain bread, etc.
- Legumes: Beans (black beans, kidney beans, chickpeas), lentils, peas, etc.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, cashews, chia seeds, flaxseeds, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, etc.
- Lean Proteins: Chicken breast, turkey breast, lean beef, fish (salmon, tuna, trout), tofu, tempeh, legumes, etc.
- Healthy Fats: Avocado, olive oil, coconut oil, flaxseed oil, nuts, seeds, fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), etc.
- Dairy and Dairy Alternatives: Greek yoghurt, cottage cheese, almond milk, coconut milk, etc.
- Herbs and Spices: Basil, oregano, parsley, cilantro, garlic, ginger, turmeric, cinnamon, etc.
- Sweeteners: Honey, maple syrup, stevia, etc. (used in moderation).
- Beverages: Water, herbal teas, green tea, etc.
- Other: Eggs, unsweetened cocoa powder, vinegar (balsamic, apple cider), etc.

The world is awakening
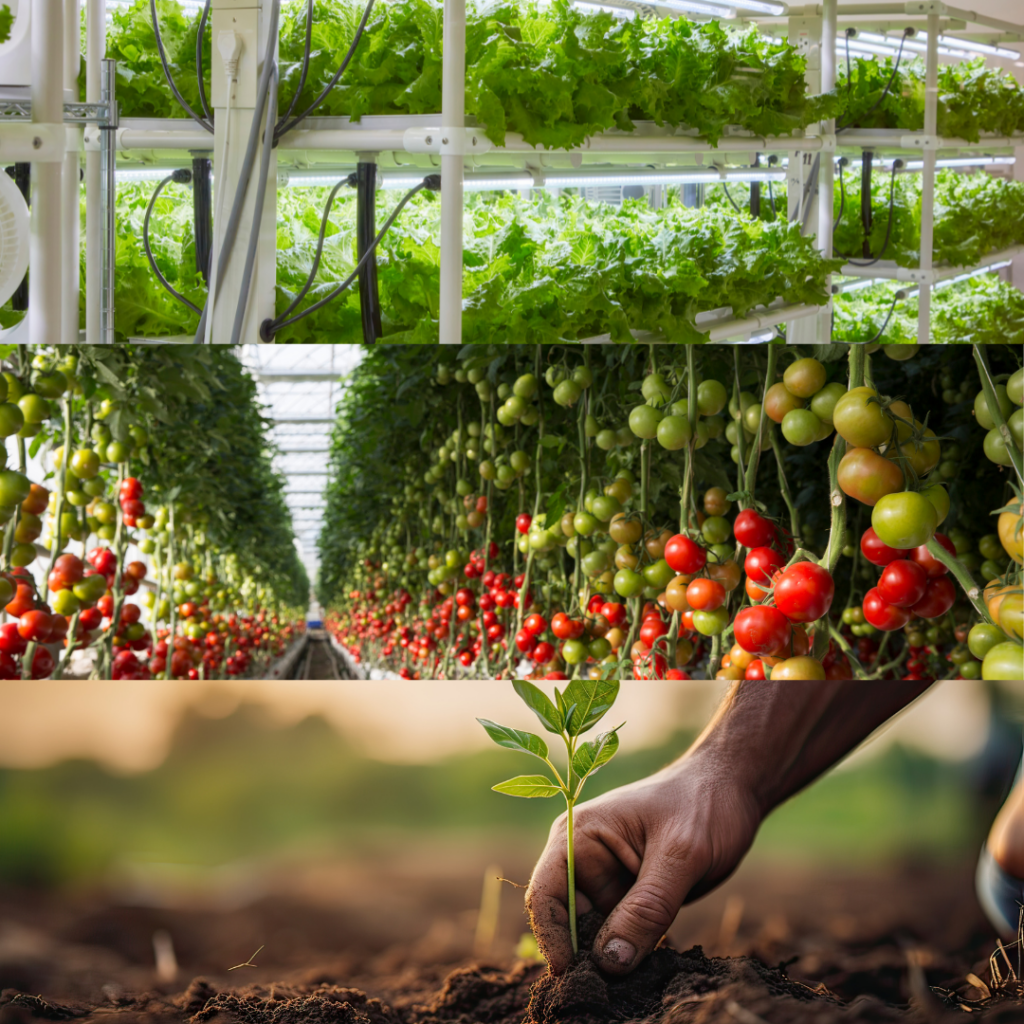
In recent years, there has been a notable increase in the number of people who are curious about the foods they eat and where they come from. An increasing understanding of the links between nutrition, health, environmental sustainability, and social justice is reflected in this movement. More people are looking for transparency in the processes involved in producing food. This includes the cultivation of crops, the care of animals, and the distribution and processing of food. Many people are calling for a return to more natural and whole food options due to health concerns. Furthermore, there is a growing interest in promoting regional and sustainable food systems. These place an emphasis on organic farming, small-scale farming, and humane treatment of animals. The trend towards mindful eating is motivating individuals to make decisions that are in line with their morals and the creation of a more sustainable, healthy future.
The future for food production
Future food production will focus more on technology and sustainability. In order to grow crops using fewer water and pesticides, farms will employ innovative techniques. There could be an increase in foods made from plants and even lab-grown meat. There will be a decrease in food waste and a greater emphasis on producing nutritious food. In general, utilising clever ideas to feed more people will be the focus of food production in the future.


